Helpful Summary
- Overview: This article explores the differences and similarities between electronic signatures and digital signatures.
- Why Trust Us: We’ve helped 61,000+ businesses e-sign millions of documents since our founding in 2019.
- Why It Matters: E-signatures and digital signatures are different tools that serve different purposes, offer different levels of security, and have different legal implications.
- Action Points: Electronic signatures can refer to a wide range of virtual signatures that use various methods to verify the signer’s identity. Digital signatures specifically use encryption technology to verify the authenticity and integrity of a document.
- Further Research: Check out our e-signature guides for tool recommendations, insights, and more.
The terms “electronic signature” and “digital signature” often get used interchangeably—but they aren’t actually the same thing. In fact, they’re often referring to completely different technologies used for completely different purposes.
So which is better? Is there a clear winner? Which one should you be using in your specific situation?
In this SignWell guide, we’re demystifying the differences between these two types of signatures so you can confidently choose which one is right for your business and document needs.
Let’s get started.
Why Listen To Us?
At SignWell, we’ve helped over 61,000 businesses streamline their document workflows with powerful, flexible e-signing features. We’ve seen first-hand the impact that electronic and digital signatures can have on businesses of all sizes.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences between these two types of signatures and help you determine which one is best for your specific use case.
Electronic Signatures vs. Digital Signatures: An Overview
Before we go into a more in-depth discussion, here’s a quick overview of the differences between digital and electronic signatures.
“Electronic signature” is an umbrella term used to describe the act of signing documents electronically. It can include a variety of methods, like typing your name, using a stylus or finger to sign on a touch screen, or even just clicking an “I agree” button.
A “digital signature” is a specific kind of electronic signature that uses a unique digital code to verify the identity of the signer and ensure the integrity of the document. It provides an added layer of security and authenticity.
Both of these tools work well in different contexts.
What Is an Electronic Signature?
An electronic signature (or e-signature) is used to verify that someone has agreed to a document without a physical signature (or wet signature). As you may have noticed, that’s a pretty broad definition—“electronic signature” is an umbrella term that encompasses many types of electronic verification.
These can include:
- Typing in your name or initials in a text field
- Uploading an image of your signature
- Using a stylus or finger to sign on a touchscreen device
- Clicking an “I agree” button
- Checking a box that says, “I accept the terms and conditions”
… and more.
All of these methods are taking the place of a physical signature on paper. That said, not all are legally binding—many electronic signature methods fall on a spectrum of security and legality (with digital signatures being one of the most secure and legally binding).
To be legally binding, electronic signatures often need to be compliant with a range of international and industry-specific requirements and standards (like HIPAA, SOC 2 Type 2, ESIGN, eIDAS, and more).
Example of an Electronic Signature
SignWell is an example of a tool that collects secure, legally binding e-signatures.
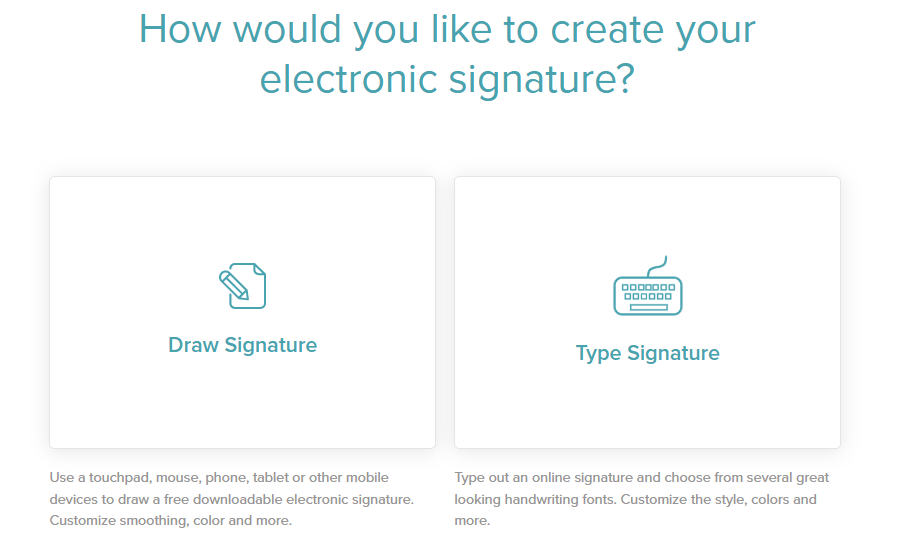
Signatories can choose to type out their signatures or draw them. When a signature is added to a signature field on a document, it becomes legally binding thanks to SignWell’s strict compliance with regulations like:
- ESIGN
- eIDAS
- UETA
We also offer features like bulk signing, audit trails, and anti-tamper protections that improve efficiency without sacrificing security or legality.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electronic Signatures
Advantages
- Simplicity: Electronic signatures are simple enough for anyone to understand, while still offering a legally binding alternative to wet signatures. With a tool like SignWell, signatories can access and sign documents on any device without downloading any apps or creating an account.
- Efficiency: Electronic signatures offer a streamlined way to sign documents, as they eliminate the need for printing, scanning, and mailing. That said, some methods are more efficient than others—SignWell’s electronic signatures are designed for maximum efficiency, while digital signatures are designed for maximum security.
- Convenience: With electronic signatures, there is no need to physically meet with other signatories or send documents back and forth. This makes the process much more convenient and time-saving for all parties involved.
Disadvantages
- Struggles With Complexity: Some e-signature tools struggle when dealing with complex workflows and documents. This can lead to errors and delays in the signing process, causing frustration for users.
- Security Concerns: While electronic signatures are generally secure, there is always a risk of hacking or tampering with the document during the digital transfer process. It’s important to choose a reputable e-signature service that prioritizes security and encryption measures.
- Legal Validity: While most countries recognize electronic signatures as legally binding, there may be limitations depending on the type of document being signed and the industry. In those niche cases, more advanced forms of electronic signatures like AES, QES, and digital signatures may be necessary.
What Is a Digital Signature?
Digital signatures are a special type of electronic signature that use encryption to ensure the integrity of a document. They’re typically used for sensitive transactions or documents that require high levels of security and authentication—think government documents, financial transactions, or legal contracts.
How do digital signatures work? Using digital “fingerprints.”
When a digital signature is applied to a document, it creates a unique code that’s linked to the signer’s identity and cannot be replicated. This code acts as a “fingerprint” for the document—by comparing the code to the original, it’s immediately obvious if any changes have been made.
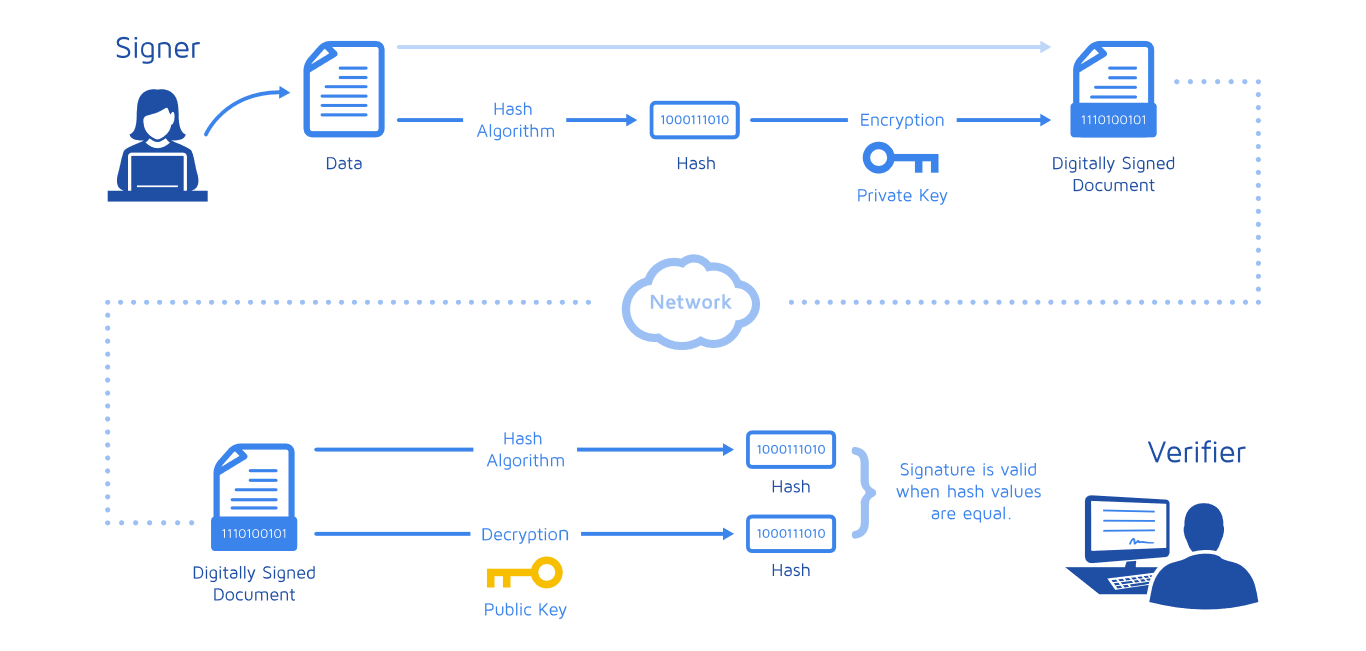
In other words, a digital signature doesn’t look like a signature at all (although it may be attached to one). Instead, it’s a series of numbers and letters that represent the signer’s identity and confirm the document has not been tampered with.
Example of a Digital Signature
Acrobat Sign is a tool that supports digital signatures.
Before you can add your digital signature to a document, you’ll need to get a certificate-based digital ID by providing one or more digital identity certificates (passports, bank statements, etc.) from trusted third parties (governments, banks, etc.). This digital ID is then linked to a unique, unreplicatable digital signature.
Once you have your digital ID, adding a digital signature is as simple as clicking the “Sign” button in Acrobat Sign. You can then choose to draw or upload your electronic signature, and once added, it will be encrypted and securely attached to the document.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Signatures
Advantages
- Secure: Digital signatures are one of the most secure forms of electronic signatures. The steps required to verify each signer’s identity make it difficult to counterfeit or manipulate.
- Legally Binding: Digital signatures are legally recognized as valid forms of signature in most countries around the world. If you’re in doubt about the legality of an electronic signature, the odds are pretty good that digital signatures will be accepted.
- (Eventually) Efficient and Convenient: Once you’re past the initial verification, digital signatures are just as convenient as any other form of electronic signature. However, the verification process can be time-consuming, especially for first-time users.
Disadvantages
- Time-Consuming: Digital signatures aren’t well-suited for routine contracts and agreements due to the amount of time it takes to verify the identity of the signer. This makes it difficult for individuals or businesses who frequently require signatures on documents. An overreliance on digital signatures can also hurt turnaround times due to signatory confusion, verification issues, and technical difficulties.
- Expensive: Lastly, the costs associated with digital signatures are often much higher than with simpler forms of electronic signatures. For example, GlobalSign charges $369/certificate/year, while SignWell charges $8/month for unlimited electronic signatures.
Key Differences Between Digital Signatures and Electronic Signatures
Purpose
Electronic signatures are designed to act as digital stand-ins for wet signatures. They’re intended to be flexible, efficient, and legally binding in the vast majority of cases. Tools like SignWell exhibit this purpose with a range of time-saving features, like:
- Bulk Sending
- Signing Orders
- Automated Reminders
- Integrations
- API Access
Digital signatures are designed to be secure above all else. This makes them ideal for companies that operate in highly sensitive or regulated industries, like financial services or government.
Security
Electronic signatures use a wide range of security measures to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the signed document. For example, SignWell uses audit trails that capture timestamps, IP addresses, and other data to track the signing process.
Electronic signature solutions that offer Advanced or Qualified Electronic Signatures (AES and QES, respectively) use security measures like digital certificates and biometric authentication.
Digital signatures sit on the “more secure” side of the electronic signature spectrum.
Convenience
Standard electronic signatures like the ones we offer at SignWell offer the best balance between convenience and security. They’re easy to use and can be signed from anywhere, at any time (as long as you have an internet connection).
Digital signatures are more secure, but that comes at the cost of convenience. They aren’t the type of electronic signature to use for day-to-day document signing. Instead, they are more suited for highly sensitive documents that warrant (or require) an extra level of security.
Conclusion
To quickly summarize, electronic signatures are a broad category that encompasses both standard electronic signatures, digital signatures, and everything in between.
A standard electronic signature is a digital representation of a written signature. It’s commonly used in day-to-day document signing and is easy to use, convenient, and legally binding. On the other hand, a digital signature is a more secure and advanced form of electronic signature that uses encryption technology to verify the signer’s identity and ensure document integrity.
Looking for an affordable, intuitive tool for collecting e-signatures? SignWell has helped 61,000+ businesses streamline their document signing process with features like bulk sending, signing orders, and document automation.
Sign up for free today.
Sign with a team that knows what you need.
Putting a signature on a document shouldn’t be hard. The SignWell mission? Simplify how documents get signed for millions of people and businesses.
Get Started Todaybusinesses served, so far...
total documents signed
customer support satisfaction