A digital signature is a virtual foot stamp that proves someone’s consent to digital assets like pdfs, images, cryptocurrency, and so on. We call them virtual foot stamps because digital signatures leave audit trails that show exactly who signed a document, plus where and when they signed it, and even if they tampered with it.
To do that, digital signatures use unique “keys” assigned to each individual or organization (PKIs) and a form of math called asymmetric cryptography.
In this article, we’ll learn:
- What makes up a digital signature.
- How digital signatures work.
- When digital signatures are used.
- And the benefits of using digital signatures.
Let’s get started.
What makes up a digital signature?
A valid digital signature comprises three things; a hashing algorithm, public-key encryption, and a trusted digital certificate issuer.
1. A Hashing Algorithm
A Hashing Algorithm is software that converts data like documents, images, or videos into a long string of random characters called “Hash value”, hash sum or digest.
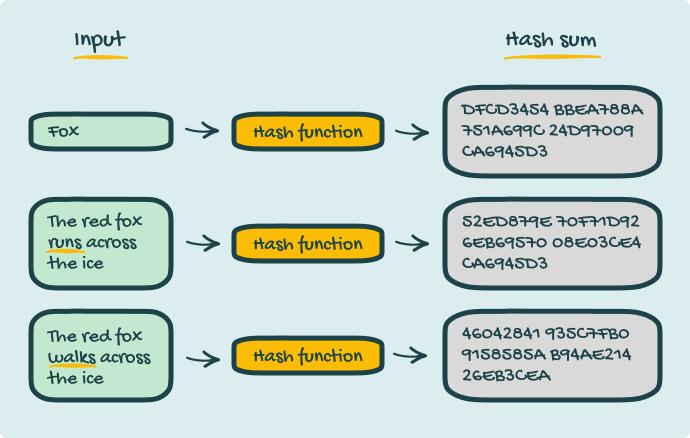
Source: Free Code Camp
Here’s how it works:
- A digital signature software converts the data on a ready-to-be-signed document into code or a “hash value” using a hashing algorithm.
- When you send the document to a receiver, the digital signature software sends an unhashed document and the hash value — to maintain a record of the contents of the original document you sent.
- The receiver signs the document, and it gets hashed again.
- At this point, your document either has two versions of the exact same hash (to signify that the receiver did not tamper with the document), or two different hash codes which would show that they changed the document.
2. Public Key Encryption
Public key encryption also known as Asymmetric encryption is a process of using two related key pairs to encrypt and decrypt a message.
Here’s how it works:
- When using digital signatures, each person gets a public and private key.
- The public key is well, public, everyone knows it. The private key on the other hand is only accessible to the unique user.
- The public key is used to encrypt the document to be signed and only the corresponding private key can decrypt the message.
- As long as the private key is not compromised, it shows that the right person received and signed the document. Because if the signed document is encrypted with a private key, only the corresponding public key can decrypt it.
3. A Trusted Digital Certificate Issuer
Digital certificates are documents that show the owner of a public key by performing extra authentication processes.
A trusted digital certificate issuer is a certified company that issues digital certificates to people. So the sender knows he’s using the right public key to encrypt the document using a digital certificate.
To verify the owner of a public key, a digital certificate authority will require the public key owner to submit his IDs, Bank documents or other identification documents.
How do Digital signatures work
Digital signatures work by hashing the document to prove that it wasn’t modified. The hashed document is then encrypted with the receiver’s public key.
When the document gets to the receiver, if it’s the right person, he can use his private key to decrypt it, and sign the document.
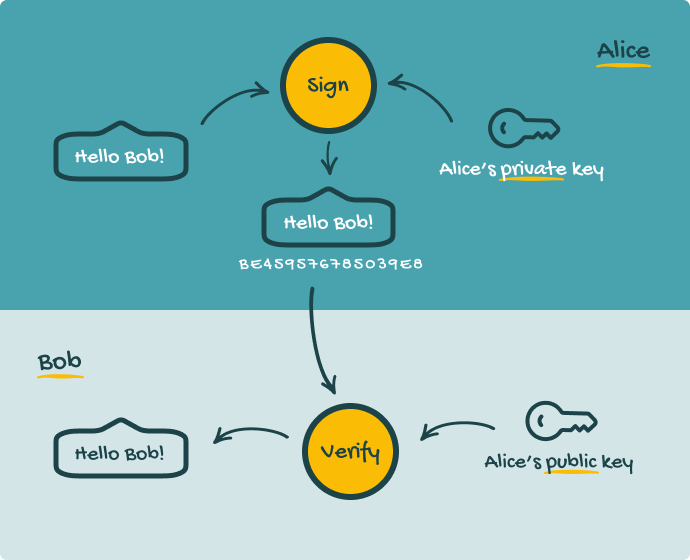
Digital signatures also go through yet another verification process to ensure authenticity. Digital certificate authorities verify that a public key belongs to the receiver through authentication steps like IDs cards, Bank statements, etc.
When are Digital Signatures used?
People use digital signatures when distributing software, in financial transactions, and in the healthcare industry. While these are not the only use cases, these are the most common places where digital signatures are used.
Software distribution
Digital signatures can validate that the particular software you’re downloading is from the original developers and not a bug, virus or clone. The developers would hash the code of the software, encrypt it with their private key, make their public key “public” via a trusted certification authority and the end user can decrypt to ensure their downloading the right software. It’s the reason you can’t use paid software for free.
Financial transactions
Digital signatures are used to verify that a particular user sent money (crypto for example) to the right person via their private key and wallet address. It’s also used to track the authenticity of the transaction; if someone changed the transaction details, for example.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers use digital signatures to provide medical services virtually. The hospital and patients use digital signatures to ensure that the medical information, medical records, and treatment provided is by the correct individual and the content is unchanged.
7 Benefits of using Digital Signatures
There are many benefits of using digital signatures for signing documents. Here are the 7 most important benefits:
- Integrity: Hashing algorithms will throw up different hash values for the same document if anyone tempers with the document.
- Authenticity: Digital signatures use both public keys and private keys to encrypt a document making it near impossible for the wrong person to sign the document. Also, certified authorities ensure that the public key belongs to the claimed sender.
- Enhanced security: Digital signatures use cryptography to authenticate and verify the content of a document. Cryptography makes it very hard for an imposter to replicate a digital signature and it also makes the content of the documents almost impossible to tamper with.
- Globally accepted: Digital signatures are globally accepted except in countries like Afghanistan, Cambodia, Cuba, Dominica, Fiji, Iran, Iraq, Laos, Mongolia, Nepal, and North Korea So you don’t have to worry about legality unless you’re from or partnering with someone from the countries mentioned above.
- Time-saving: Digital signatures allow multiple parties to sign a document without having to be physically present in the same location. It also allows signatories to sign documents at any time of the day from a preferred device.
- Cost-effective: You spend less money printing papers, and transporting to the signing venue when you sign digitally.
- Eco-friendly: Papers are harmful to the environment but digital signatures reduce the use of paper to sign documents.
FAQs about Digital Signatures
The concept of digital signatures is still new to many people. Here are some frequently asked questions about digital signatures and their answers.
What are the types of digital signatures?
There are four types of electronic signatures, two of those use digital signatures; the Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signature (QES). Both types of digital signatures use cryptography to sign and verify documents or digital assets, but QES provides an additional layer of identification verification and security compared to AES. It does this by using special qualified certificates and taking place on qualified devices.
Are digital signatures legal?
Digital signatures are legal in all US states, as well as countries like Canada, South Africa, Algeria, Turkey, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria etc. You should note that some countries require that the digital signature must have digital certificates before they are considered legal, but some others don’t.
When are electronic signatures used versus digital signatures?
Electronic signatures are used when signing documents and agreements. Digital signatures on the other hand, are used in things like when distributing software where identification of the signer and integrity of contents of the message are the primary things that matter. Digital signatures are missing the other parts that electronic signatures handle (showing intent and electronic signature consent)
Which is more secure: an electronic signature or a digital signature?
A digital signature can be more secure than an electronic signature when the electronic signature doesn’t require the use of encryption. This is because digital signatures are encrypted using mathematical functions. When an electronic signature has digital signatures in use, both can be equally secure.
How are digital signatures verified?
Digital signatures are verified using the Public Key Cryptography. Public key Cryptography uses two related keys, a private key and public key, the sender uses the receiver’s public key to encrypt the signed document and only the corresponding private key can decrypt it.
Is a scanned signature called a digital signature?
No, it isn’t. A scanned signature is a very simple form of an electronic signature that doesn’t validate the content of the document nor the signer –because it’s signed outside of the digital or electronic signature software.
Can a wet signature be digital?
No, a wet signature cannot be digital. Digital signatures must show that the content of the information hasn’t been tampered with and the right person signed the document and this is done by hashing and encrypting the message but a wet signature is simply using a pen or a seal to sign a physical document.
Start Signing Digitally for More Security and Convenience
The world is becoming more digital, remote, and fast-paced by the minute. It would be time-consuming to keep using hand written signatures to legally bind documents. If you are looking to simplify your signing process, signing digitally with electronic signatures is the way to go. They are difficult to forge, the documents are secure, and they do not require your physical presence to sign documents.
Sign with a team that knows what you need.
Putting a signature on a document shouldn’t be hard. The SignWell mission? Simplify how documents get signed for millions of people and businesses.
Get Started Todaybusinesses served, so far...
total documents signed
customer support satisfaction